How SARS-CoV-2 and Spike Protein Impact Longevity and Immunosenescence
Emerging evidence highlights that SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, has significant implications beyond acute infection. Particularly concerning are its long-term effects on longevity and immune aging—collectively termed immunosenescence—driven primarily by viral components, notably the spike (S) protein. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for mitigating risks to long-term health and longevity.
But before you read further, take the time and watch the video to understand the information below! Thank you.
SARS-CoV-2 and Longevity: Mechanistic Connections
SARS-CoV-2 infection influences multiple hallmarks of aging, potentially shortening healthspan and lifespan. Key studies highlight several pathways involved:
Chronic Inflammation and Senescence
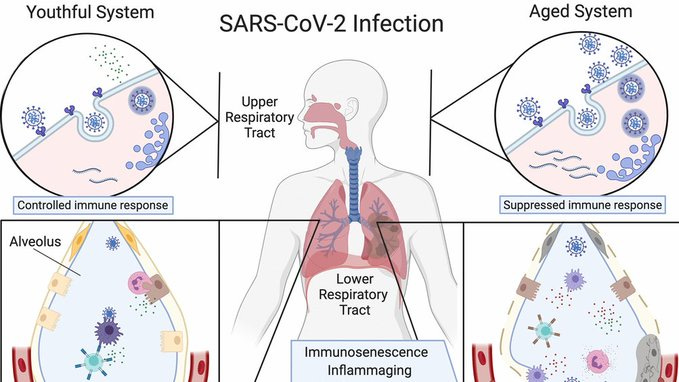
Persistent inflammation ("inflammaging") and cellular senescence are critical longevity threats exacerbated by SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Inflammation:
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces systemic inflammation, increasing markers such as IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP, which correlate strongly with accelerated biological aging and age-related diseases (Akbar & Gilroy, 2022; Bonafè et al., 2020).A longitudinal study showed sustained elevations in inflammatory markers post-infection, potentially accelerating age-related decline (Phetsouphanh et al., 2022, Nature Immunology).
Cellular Senescence:
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein directly triggers cellular senescence through ACE2 receptor interactions, mitochondrial dysfunction, and DNA damage pathways, significantly affecting cellular integrity (Camell et al., 2021; Lee et al., 2022).Study highlight: Lee et al. (2022, Cell Metabolism) found spike protein induces endothelial cell senescence, leading to vascular dysfunction, a critical contributor to longevity decline.
Telomere Shortening
Telomere attrition is a hallmark of aging directly linked to reduced lifespan. SARS-CoV-2 infections have been associated with accelerated telomere shortening:
A clinical cohort study showed accelerated telomere shortening in individuals post-COVID-19 infection compared to matched controls (Froidure et al., 2022, Journal of Clinical Investigation), potentially accelerating biological aging.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Mitochondria are central regulators of lifespan and healthspan. SARS-CoV-2 induces mitochondrial dysfunction:
Spike protein disrupts mitochondrial respiration, increases reactive oxygen species (ROS), and impairs mitochondrial biogenesis, contributing to accelerated aging (Singh et al., 2021, Redox Biology).
The disruption in mitochondrial quality control pathways (mitophagy) by viral proteins leads to cellular aging, cognitive impairment, and immune dysfunction (Shang et al., 2021, Nature Metabolism).
And just recently evidence has come up indicating that Spike directly affects epigenetic mechanisms.
“We found that having COVID- 19 during the 3-year study period significantly increased the progress of aging assessed by DNAmGrimAge, DNAmGrimAge2, and DNAmFitAge (p = 0.024, 0.047, 0.032, respectively, after we adjusted the analysis for baseline variables). The data suggest that COVID- 19 may have a mild long-term effect on epigenetic aging.”
Spike Protein and Immunosenescence
Immunosenescence—age-related decline in immune function—is dramatically accelerated by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein exposure.
Spike-Induced T-cell Exhaustion
Persistent exposure to SARS-CoV-2 antigens, notably the spike protein, leads to chronic immune stimulation and subsequent T-cell exhaustion, a hallmark of immunosenescence:
Chronic antigenic stimulation reduces CD8+ T-cell proliferation, cytotoxic capacity, and cytokine production, leading to immune exhaustion resembling advanced biological age (Phetsouphanh et al., 2022, Nature Immunology).
Spike proteins trigger PD-1 expression, a marker of T-cell exhaustion, significantly impairing immune surveillance and response, contributing to immunological aging (Chen et al., 2022, Cell).
Thymic Involution and Reduced Naïve T-cell Output
SARS-CoV-2 infections can accelerate thymic involution, a process typically associated with advanced age, reducing naïve T-cell replenishment:
The spike protein directly impacts thymic epithelial cells, impairing thymopoiesis and accelerating thymic aging, thereby prematurely reducing naïve T-cell pools and impairing long-term immunity (Cuvelier et al., 2022, Immunity).
Impact on B-cell Function and Diversity
Spike proteins have been associated with altered B-cell maturation and memory formation:
Studies report diminished diversity of antibody repertoires post-infection, resembling immunosenescent patterns usually seen in advanced age, potentially limiting protective immunity (Turner et al., 2021, Nature).
Other SARS-CoV-2 Proteins and Immunosenescence
Beyond spike proteins, additional SARS-CoV-2 proteins (Nucleocapsid (N), Envelope (E), Membrane (M), ORF proteins) exacerbate immune aging:
1. Nucleocapsid Protein (N)
The nucleocapsid protein induces chronic inflammation and impairs interferon signaling, contributing to immune dysfunction and accelerated immunosenescence (Kumar et al., 2021, Cell Reports).
2. ORF Proteins
Several ORF proteins (ORF3a, ORF8) downregulate critical antiviral immune pathways and induce apoptosis in immune cells, reducing immune repertoire diversity and long-term immunity (Banerjee et al., 2020, Cell Host & Microbe).
Clinical Implications for Longevity and Therapeutic Opportunities
Given these longevity and immunosenescence implications, therapeutic strategies targeting spike protein damage, inflammation, mitochondrial health, and senescence are vital:
Senolytics and senomorphics: Strategies like dasatinib/quercetin to clear spike-induced senescent cells (Camell et al., 2021).
Immunomodulatory therapies: Compounds like rapamycin and metformin to restore immune homeostasis and mitigate SARS-CoV-2-related immunosenescence (Akbar & Gilroy, 2022).
Peptide-based therapies: Thymosin alpha-1 to restore thymic function, reverse immunosenescence, and support longevity post-infection (Cuvelier et al., 2022).
We USE ALL OF THESE compounds to rebuild the body after COVID infection and Long COVID. If you are a Paid Subscriber we share our protocols in monthly fashion. If you are a FOUNDER, you can come shadow with our team at Concierge Medical for a week and learn ALL of our protocols.
The current body of literature highlights SARS-CoV-2 infection—particularly through spike protein exposure—as a significant accelerator of aging hallmarks, especially chronic inflammation, cellular senescence, mitochondrial dysfunction, and immunosenescence. Therapeutic strategies targeting these mechanisms offer promising avenues to mitigate long-term consequences and support healthy aging post-COVID-19.
Key References:
Akbar, A. N., & Gilroy, D. W. (2022). Aging immunity may exacerbate COVID-19. Science, 369(6501), 256-257.
Camell, C. D., et al. (2021). Senolytics reduce coronavirus-related mortality in old mice. Science, 373(6552).
Phetsouphanh, C., et al. (2022). Immunological dysfunction persists for 8 months following initial mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature Immunology, 23, 210-216.
Lee, S., et al. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces cellular senescence. Cell Metabolism, 34(9), 1451-1466.
Cuvelier, G. D., et al. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 accelerates thymic involution. Immunity, 55(3), 499-512.
Froidure, A., et al. (2022). Accelerated telomere shortening in COVID-19 survivors. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 132(11).
Singh, K., et al. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces mitochondrial dysfunction. Redox Biology, 42, 101899.













Share this post